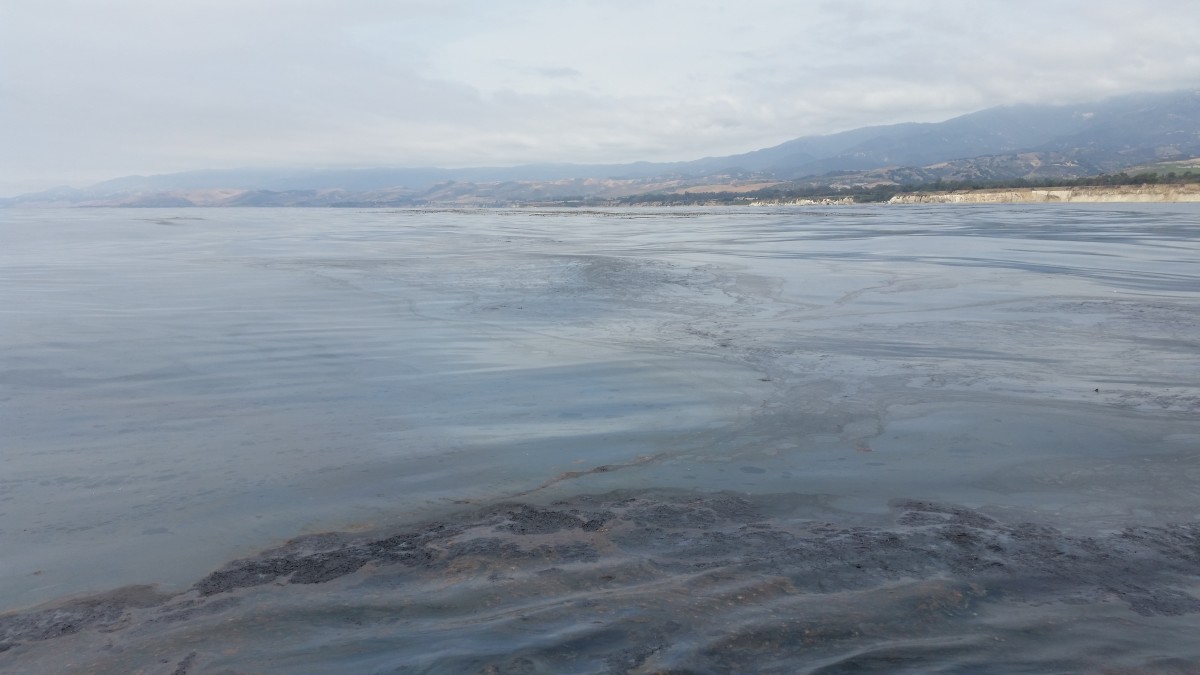
Natural seepage of hydrocarbons from the ocean floor in the northern santa barbara channel has been significantly reduced by oil production according to two recently published peer reviewed articles one in november s geology magazine the other in the journal of geophysical research oceans.
Does oil seep from the ocean floor.
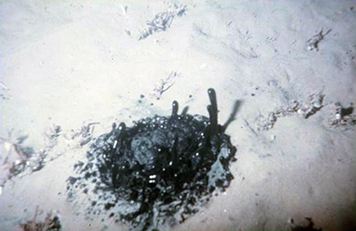
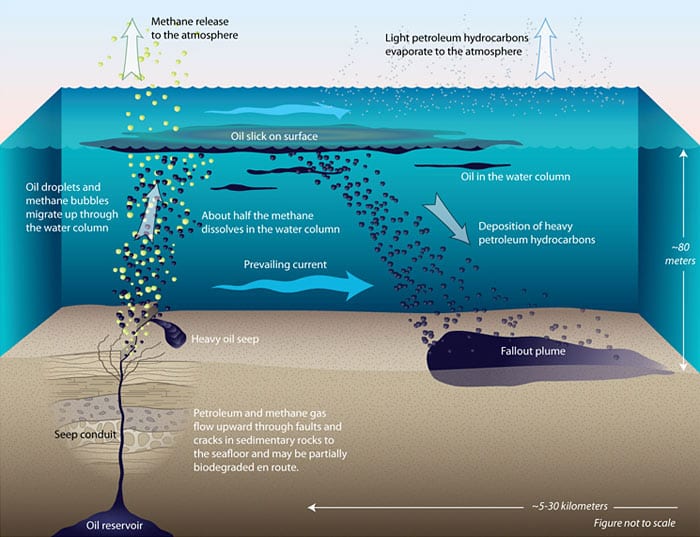
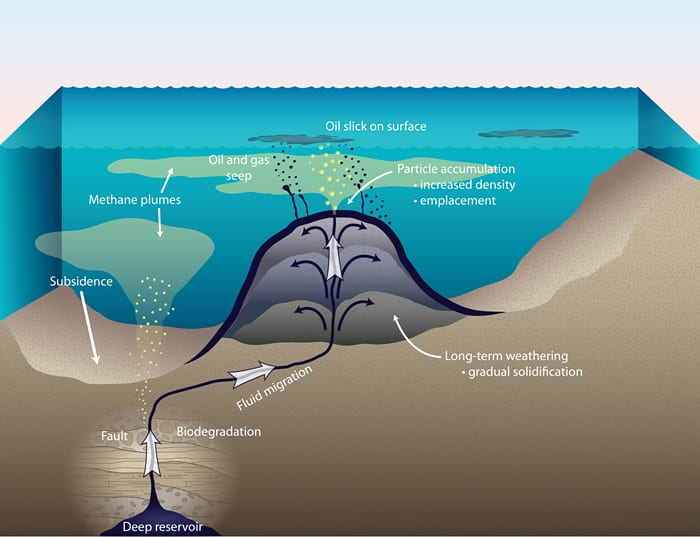
Weathering and the fallout plume of heavy oil from strong petroleum seeps near coal oil.
While the amount of oil and its ultimate fate in such manmade disasters is well known the effect and size of natural oil seeps on the ocean floor is murkier.
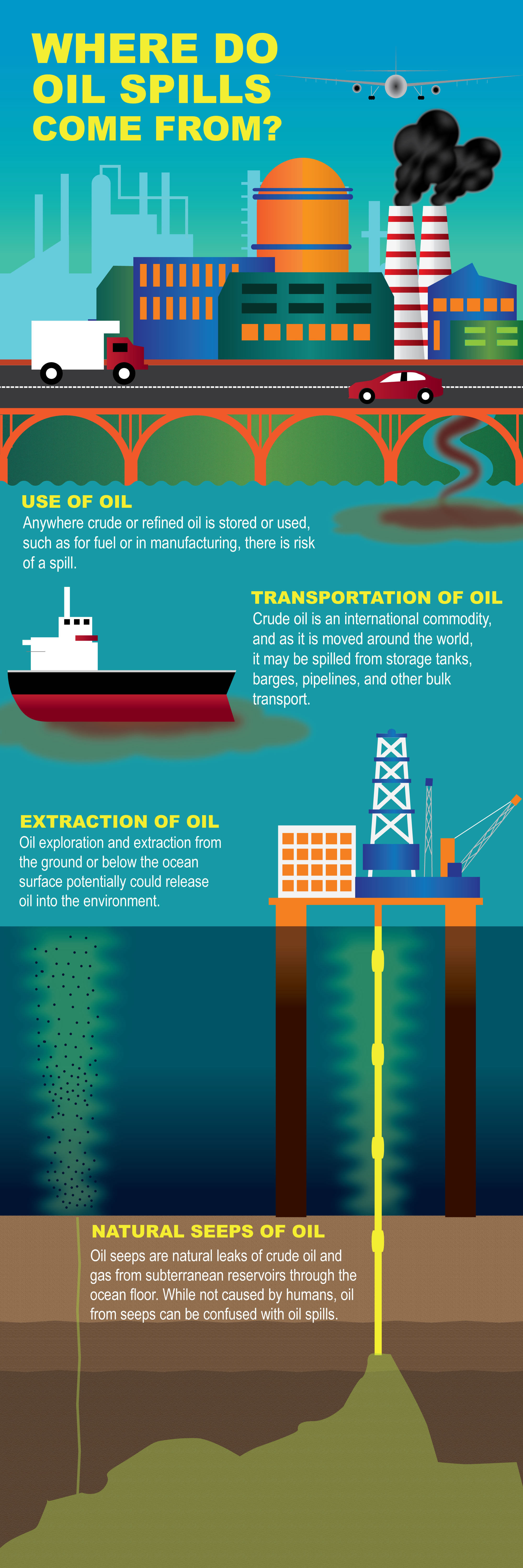
Oil wastes that enter the ocean come from many sources some being accidental spills or leaks and some being the results of chronic and careless habits in the use of oil and oil products.
Most waste oil in the ocean consists of oily stormwater drainage from cities and farms untreated waste disposal from factories and industrial facilities.
It s the amount of residual oil that made it to the ocean floor that surprised all of the researchers.
Coast guard and the u s.
A new study finds that the natural.
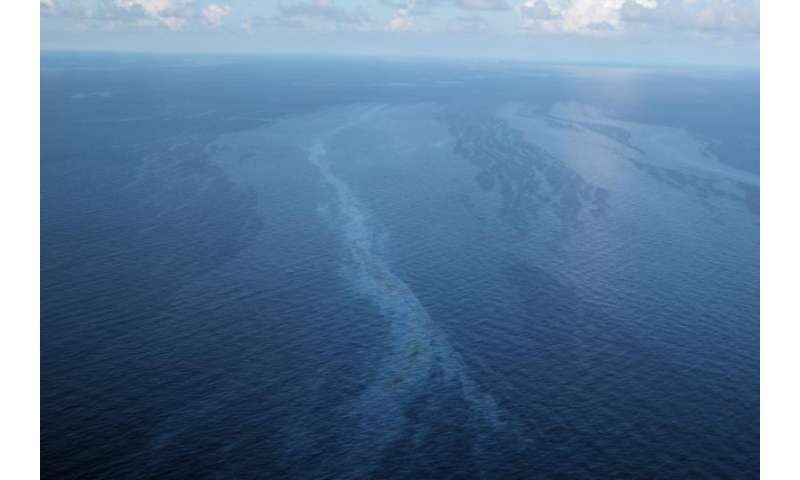
In the gulf of mexico there are more than 600 natural oil seeps that leak between one and five million barrels of oil per year equivalent to roughly 80 000 to 200 000 tonnes.
These seeps contribute about 5 million gallons of oil to the ocean annually with.
A 2003 report from the national research council estimates that on average approximately 160 000 tonnes of petroleum enter north american waters through natural seeps each year.
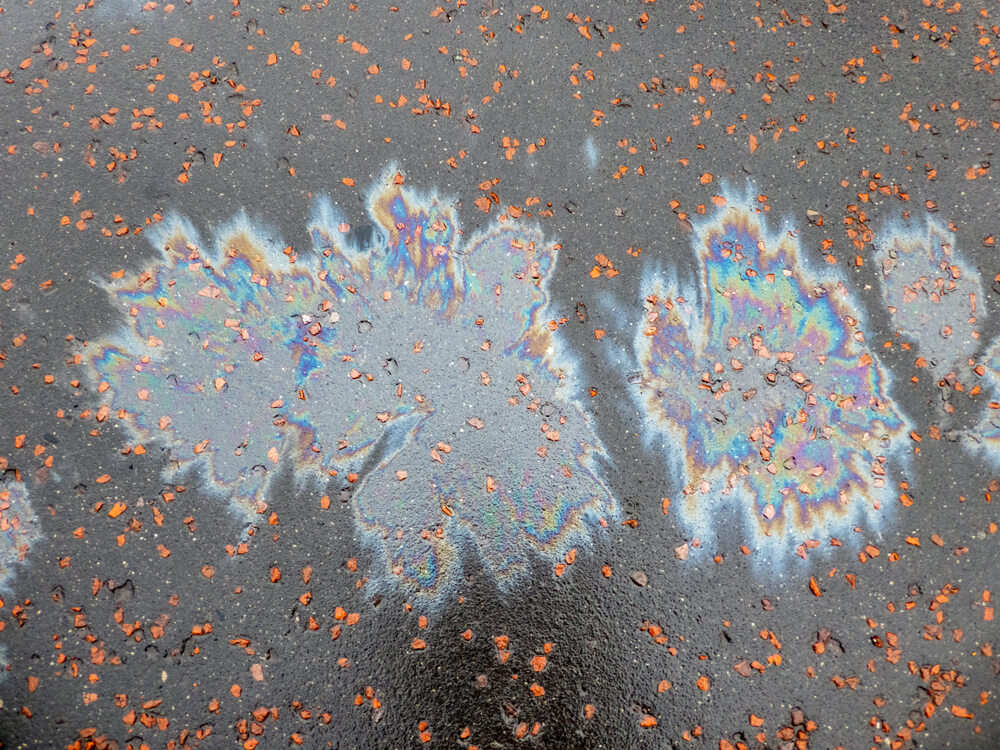
Oil can be toxic to sea life like fish sea stars shrimp and seabirds with their impacts largely concentrated in the immediate area around a seep.
The california division of oil gas and geothermal resources published a map of offshore oil seeps from point.
The waters off southern california are one area in particular which host hundreds of known naturally occurring oil and gas seeps.
Or r tracks naturally occurring oil seeps helps distinguish oil seeps from production platform leaks and other spills and works with partners like the u s.
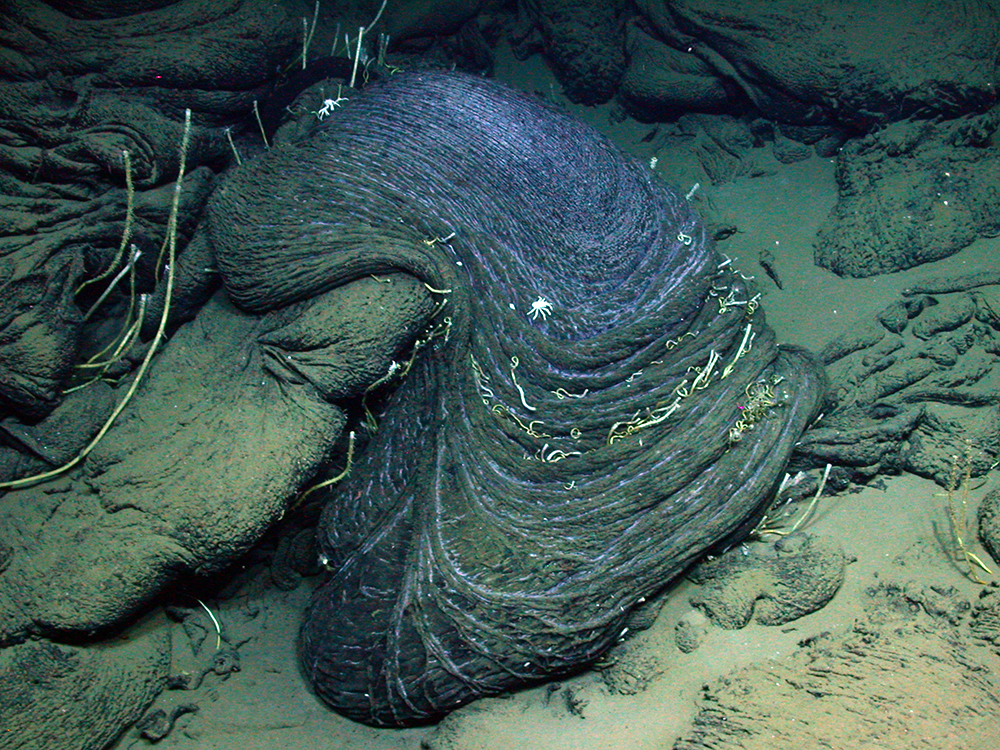
When a petroleum seep forms underwater it may form a peculiar type of volcano known as an asphalt volcano.